Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity is a term that refers to the natural variations in human brain function and embraces that people have different ways of thinking, learning, and processing information.
Specific neurodifferences include autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and DCD (dyspraxia) among others. Rather than viewing these differences as ‘deficits’, neurodiversity recognises them as valuable and necessary variations of the human experience. It advocates for acceptance, accommodation and support of neurodivergent individuals, who often possess many unique strengths and talents.
What is Neurodiversity?
It is generally understood that the term ‘neurodiversity’ was coined by Australian sociologist Judy Singer in the late 1990s. She used this term to describe the idea that neurodifference should be seen as part of normal human variation rather than as ‘disorders’.
Neurodiversity encompasses all types of thinking and processing styles, but is also sometimes used as an umbrella term for a range of neurodifferences, including autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and DCD (dyspraxia), among others.
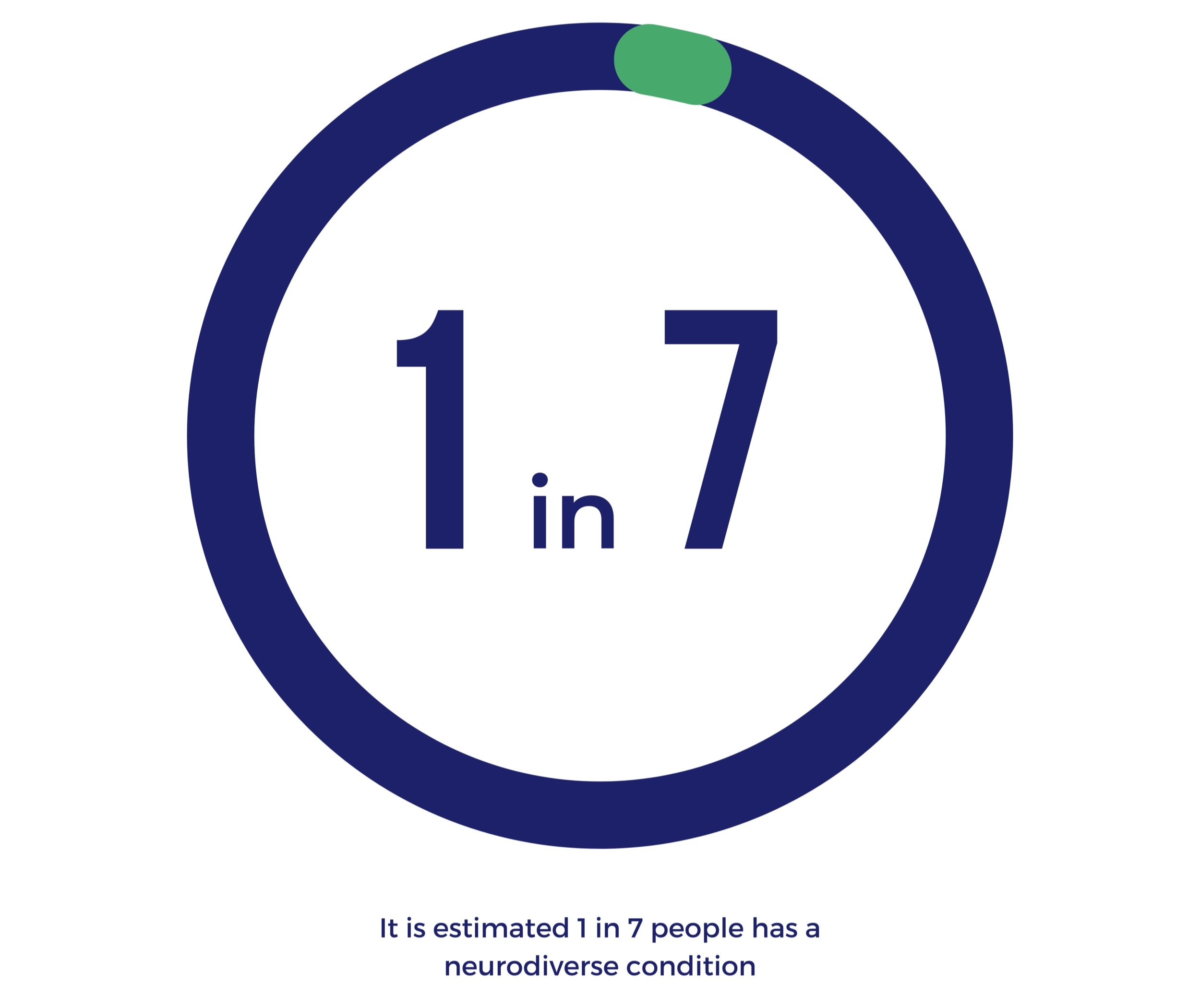
Approximately 15% of the population are neurodivergent, representing a significant proportion of existing staff, job applicants and customers
Common Strengths Associated with Neurodiversity
Many neurodivergent individuals possess a range of skills and strengths that can be an asset in a wide variety of fields and environments. These can include:
-
The ability to intensely focus on a task or project for an extended period of time without getting distracted. This skill can be helpful in jobs that require attention to detail, such as research, programming, and engineering.
-
The ability to see patterns in data and information that others may not notice. This skill can be useful in fields such as finance, where identifying trends and patterns can lead to better decision-making.
-
A tendency to think outside the box and come up with unique solutions to problems. This skill can be beneficial in fields such as art, design, and advertising.
-
An excellent memory for details and ability to recall information with ease. This skill can be useful in fields such as law, medicine, and history.
-
A keen eye for detail and ability to spot errors or inconsistencies that others may miss. This skill can be helpful in fields such as editing, proofreading, and quality control.
In addition to these skills and others, neurodivergent individuals can bring new ideas and perspectives to their workplaces, which can be highly beneficial for out-thinking and out-performing business competitors. By recognising and embracing the value of neurodiversity, organisations can create more neuro-inclusive environments where individuals can thrive.
Many people with neurodifferences possess unique skills. These skills vary from person to person, and organisations are missing out on a whole talent-pool of people by not taking the steps to become neuro inclusive
Common Neurodifferences
Learn about some of the most commonly known neurodifferences:
-
Autism is characterised by differences in how an individual communicates and engages with others, and how they experience the world around them, as well as repetitive behaviours and intense interests in specific topics or activities. Some key strengths autistic individuals may possess include hyperfocus and attention to detail, which may help them to gain expert knowledge in their field and produce work to a high standard.
-
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)is a neurodifference that is characterised by challenges sustaining or switching attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. ADHD can present differently in individuals which can make diagnosis and identifying appropriate support challenging. However, individuals with ADHD may have excellent creative thinking skills and adaptability which can be highly sought after in professional settings.
-
An estimated 10% of the population is believed to be dyslexic. Dyslexia is a neurodifference that affects a person's ability to accurately read and write. Dyslexic individuals may have challenges with spelling, recognising words, processing written information and short term memory. However, dyslexic individuals may also be creative, be able to think outside the box to solve issues, and have good emotional intelligence.
-
DCD (Developmental Coordination Disorder) is also known as dyspraxia, and is a neurodifference that affects an individual’s movement and coordination. It is estimated that 3-5% of the population have DCD, and individuals may experience challenges with tasks that require fine motor skills, such as tying shoelaces or gross motor skills, such as riding a bike or operating machines. It can also be challenging to plan and stay organised. With the right support, dyspraxic individuals can maximise their unique strengths, which may include strategic thinking skills, problem-solving abilities and resilience.
-
Dyscalculia is a neurodifference which can impact an individual’s ability to acquire, understand and use mathematical skills. Dyscalculic individuals may have challenges with mathematical calculations and concepts, as well as challenges with judging space or time. Some of the strengths and skills often associated with dyspraxia include enhanced creativity, verbal communication skills and visual thinking.
"The workplace doesn't need just one skillset or approach, and we should all recognise the value that different employees can often bring with them."
- Theo Paphitis,
Dragon from BBC’s Dragon’s Den
Neurodiversity in the Workplace
Neurodivergent individuals can bring a range of strengths and perspectives to the workplace. Lexxic recognises the importance of fostering neuro-inclusive environments, and partners with organisations to implement strategic changes that ensure all employees, regardless of their neurodifference, are valued and supported.
Benefits of Neurodiversity
Embracing neurodiversity at work can bring a range of benefits to a company. For example, autistic individuals may have exceptional attention to detail and strong analytical skills. Individuals with ADHD may have high levels of creativity and adaptability. Dyslexic individuals may have strong visual-spatial skills and a unique ability to see the big picture.
As well as these strengths, empowering neurodivergent talent can lead to increased innovation, improved productivity, and enhanced employee wellbeing. By embracing neurodiversity, organisations can tap into the full potential of all their employees and create a more inclusive and supportive workplace culture.
Challenges and Support
While there are many benefits to embracing neurodiversity, neurodivergent individuals can still face workplace challenges. To address these challenges, Lexxic can partner with organisations to provide a range of support options including neurodiversity workshops and webinars, neurodiversity awareness and individual skills e-Learning modules, and assessments for individuals at every stage of their career and throughout their personal neurodiversity journey. To understand the needs of your employees and the support and adjustments that can be put in place to help them thrive at work, we also recommend carrying out a workplace needs assessment.
Neurodiversity and Mental Health
While neurodivergent individuals often possess a range of strengths and talents, it's important to recognise that neurodivergent individuals may face mental health challenges. For example, autistic individuals may experience challenges with social interaction and communication, which can lead to feelings of isolation and anxiety. Similarly, ADHD is characterised by traits of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, which could cause challenges in academic or professional settings, and in turn potentially impact an individual’s confidence. Individuals with ADHD may also have challenges with emotional regulation.
Mental Health Challenges
It's important to recognise that mental health challenges faced by neurodivergent individuals are not necessarily caused by the traits of their neurodifferences.. Rather, these challenges are often the result of societal attitudes and structures that are not accommodating or accepting of neurodiversity.
Many neurodivergent individuals may face discrimination or stigma in their daily lives, which can lead to feelings of low self-esteem. Individuals may also face challenges accessing appropriate support and resources, such as reasonable adjustments in academic or work settings.
Support and Resources
Fortunately, there are a growing number of resources and support systems available for neurodivergent individuals who may experience mental health challenges. For example, organisations may offer Employee Resource Groups and networks to give individuals the ability to share their lived experiences and learn about other available resources, which may include access to therapy sessions.
As not all individuals may feel comfortable sharing their neurodifference at work or seeking out reasonable adjustments or accommodations, managers also have a role to play in ensuring work environments are psychologically safe and welcoming, as well as educating their teams on the value of neurodiversity in the workplace.
How Can Lexxic Help?
Lexxic is a specialist psychology consultancy. We believe that all minds belong, so it is our mission to inspire a working world that supports and values the talents of neurodivergent minds, empowering individuals to be their best
selves at work.
We partner with organisations to create neuro inclusive cultures and provide support services, so neurodivergent talent can flourish.
Our team of highly qualified psychologists provide workplace support and advice for individuals, teams and organisations. Get in touch if you would like to chat with one of our team, or find out more about the services
we can provide.